The magnitude 8.8 earthquake that struck Kamchatka, Russia, has drawn attention to one of the most dangerous and volatile regions on the planet, the Pacific Ring of Fire. The tremors and resulting tsunamis are an expression of the ongoing geological activity that affects a vast area of the Pacific Ocean. But what do we really know about the Ring of Fire? And why is Kamchatka among the areas most exposed to earthquakes and volcanic activity?
What is the Pacific Ring of Fire?
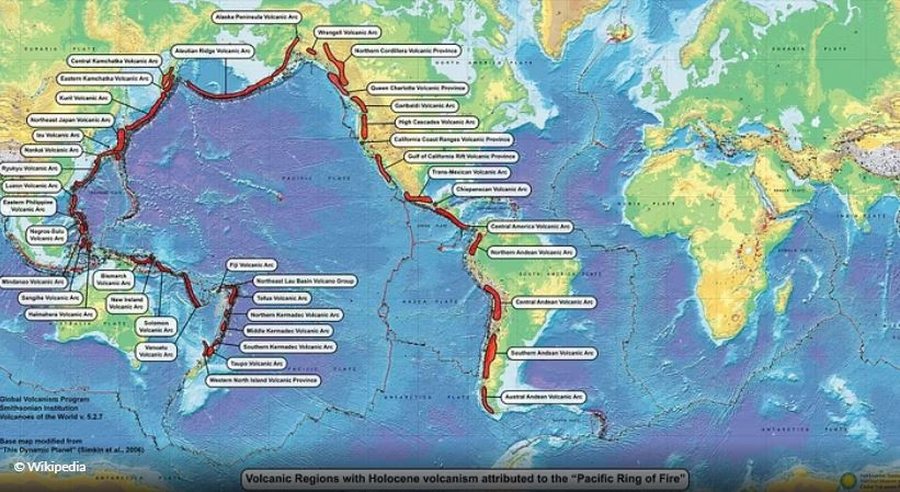
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a geological belt that encircles the Pacific Ocean for over 40,000 kilometers. It is characterized by extraordinary seismic and volcanic activity due to the presence of many tectonic plates that are constantly shifting. The main plates involved are the Pacific Plate, the North American Plate, the South American Plate, the Philippine Plate, and the Indo-Australian Plate. The most important geological phenomenon is subduction, the sliding of one plate under another, which generates deep and potentially destructive earthquakes.
Where is the Ring of Fire located?
This belt extends along the eastern coasts of Asia (Japan, the Philippines, Indonesia), Oceania (Papua New Guinea, New Zealand) and continues along the western coasts of the Americas (from Alaska to Chile). Approximately 90% of the world's seismic activity and 75% of the planet's active volcanoes are concentrated in this belt. Therefore, the Ring of Fire is a real ring of fire and instability.
Why is Kamchatka an earthquake-prone area?
The Kamchatka Peninsula lies along the subduction zone between the Pacific and Okhotsk plates, where one slides beneath the other. This movement generates enormous pressures that are released in the form of earthquakes, some of which are very strong. In addition, the area is characterized by the presence of over 160 volcanoes, 29 of which are active, including Klyuchevskaya Sopka, one of the largest in the world. The combination of tectonic movements and volcanic activity makes this region extremely unstable and is constantly monitored by scientists.
Great Kamchatka earthquakes in history
The region has experienced numerous historical seismic events:
1952: An earthquake with an estimated magnitude of 8.5 to 9.0 struck Severo-Kurilsk, generating a tsunami with waves up to 18 meters high and causing over 2,300 deaths.
2006: A magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck the eastern coast of Kamchatka, causing moderate damage.
2020: A magnitude 7.5 earthquake triggered an extended tsunami warning but caused limited damage.
2025: The recent 8.7 magnitude event has rekindled fears of the past, with tsunami waves and warnings across the Pacific.
Scientists agree that the Ring of Fire will continue to be the site of significant seismic events. Continuous monitoring, the use of advanced sensors and early warning systems are essential to reduce the risk to the population. And the Kamchatka event is another reminder of the power and unpredictability of the Earth. (A2 Televizion)











